How to Find Common Free Time in Google Calendar: Manage Shared Schedules with Google Apps Script

Have you ever found it time-consuming to search for common free time when coordinating schedules within your team?
Even though Google Calendar allows you to view multiple calendars at once, comparing everyone’s schedules side by side can quickly become confusing.
To solve this, I’ll show you how to use Google Apps Script to automatically extract shared free time slots from each member’s Google Calendar and manage them in a Google Spreadsheet.
With this method, scheduling meetings and coordinating team events becomes much easier and more efficient.
If you want to save even more time, I also offer a ready-to-use, pre-configured template (paid) in a separate article—perfect for those who want to get started right away.
For more details, check out the article below.
Example Output
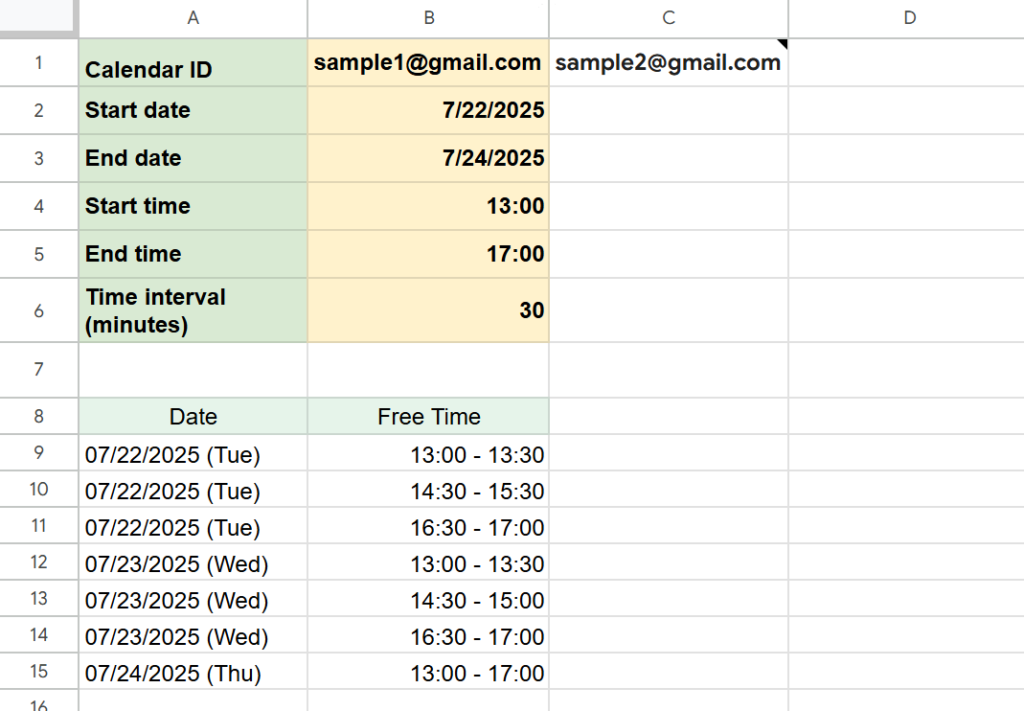
The script will display a list of shared free time slots within your selected date range.
For each day between your specified start and end dates, the spreadsheet will show the common available time slots for all participants.
Each row contains the date and a list of free time periods when everyone is available, making it easy to see which times do not overlap with any existing events across multiple Google Calendars.
This allows you to quickly find common availability for meetings or team appointments, streamlining your scheduling process.
You can also customize the interval (in minutes) for checking available time slots by entering a value in cell B6. In the example shown, free time is displayed in 20-minute increments.
What You Need to Prepare
Before creating the Google Apps Script, you’ll need to complete the following two setup steps.
If you’ve already done these, feel free to move on to the next section.
Setting Google Calendar Sharing Permissions
How to Share Your Google Calendar
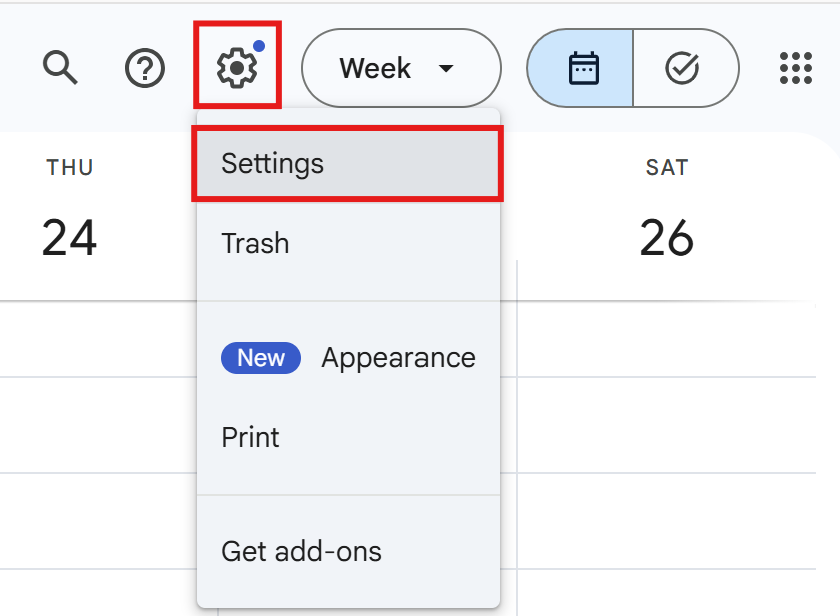
Open Google Calendar and click the settings icon in the top right corner.
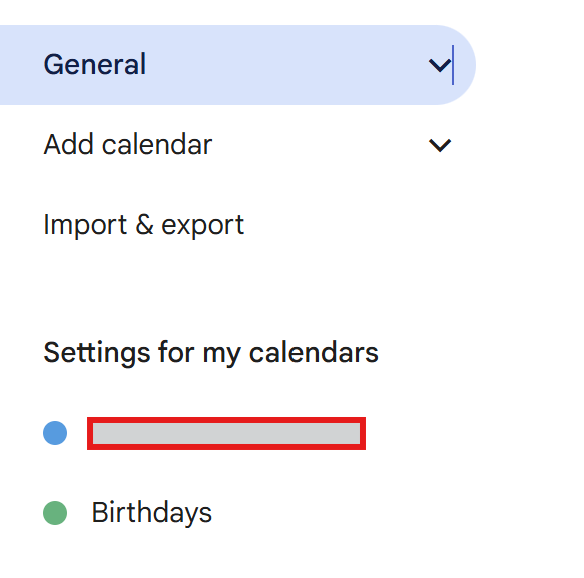
In the left-hand menu, select Settings for My Calendars and click on the calendar you want to use.
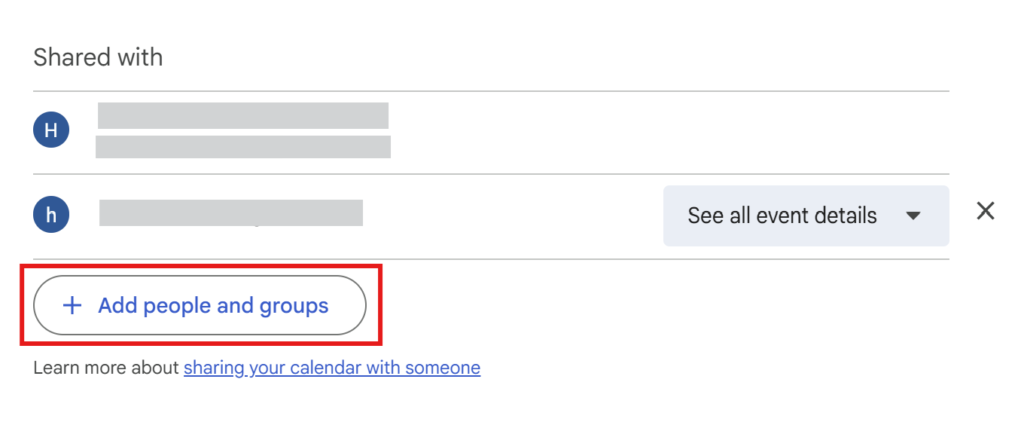
Scroll down on the calendar settings page to find Share with specific people or groups.
Click Add people or groups within this section.
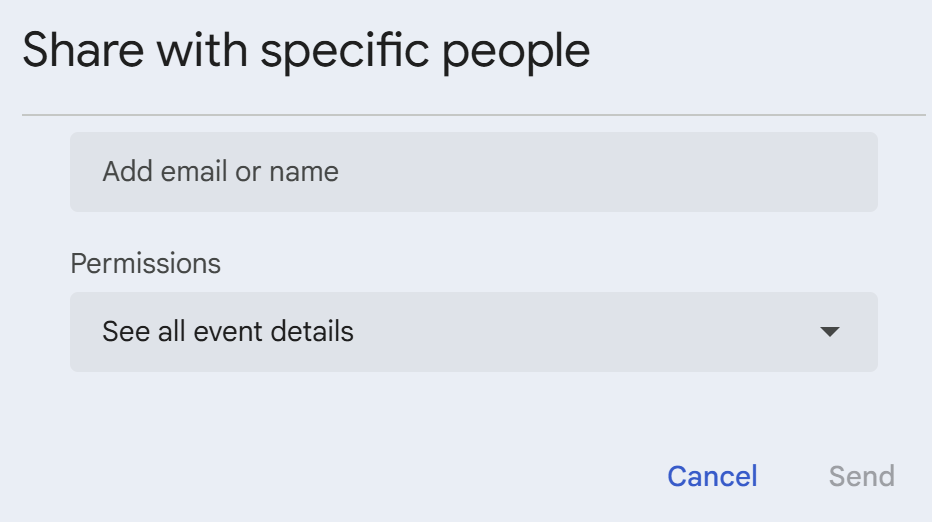
Set the permission level to See all event details and share the calendar.
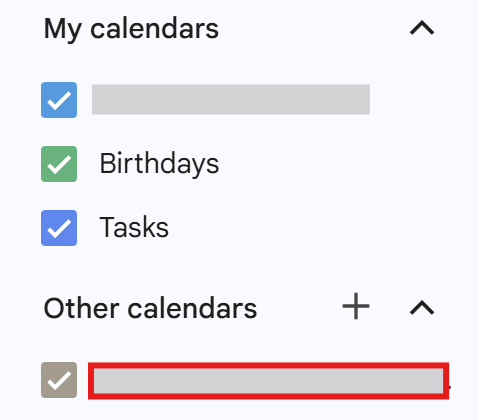
The shared calendar will be added under Other calendars in Google Calendar.
Tip:
If you don’t see the shared calendar after it’s been shared, try the following:
Go to Other calendars → + → Subscribe to calendar → Add calendar and enter the Calendar ID.
Click the sharing notification link you received via email.
How to Find Your Google Calendar ID
How to Find Your Google Calendar ID

Open Google Calendar and click the settings icon in the top right corner.

In the left-hand menu, select Settings for My Calendars and choose the calendar you want to use.
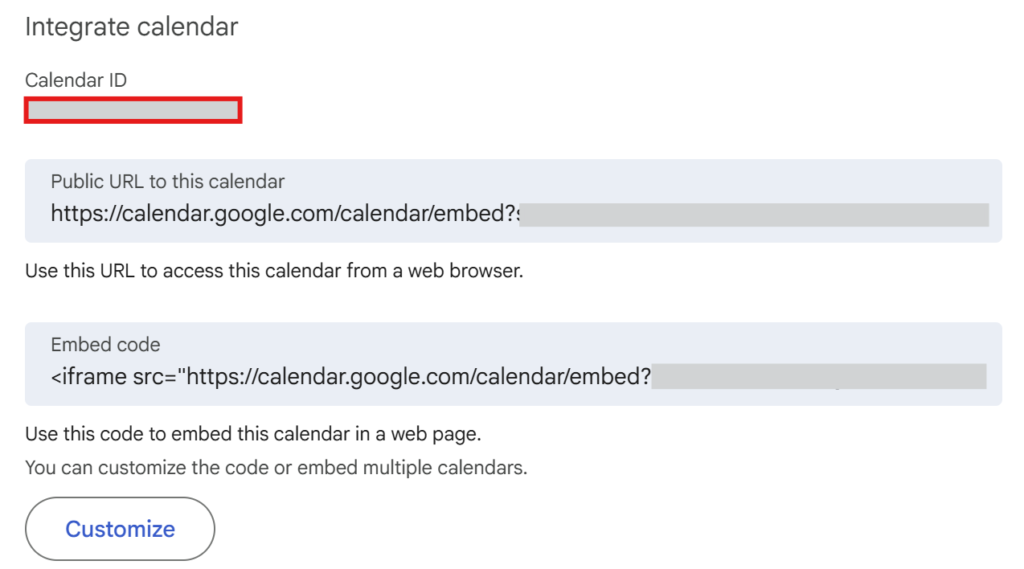
On the calendar settings page, scroll down to find the Calendar ID section.
The Calendar ID is usually in the format xxx@gmail.com or xxxx@group.calendar.google.com.
Step-by-Step Instructions
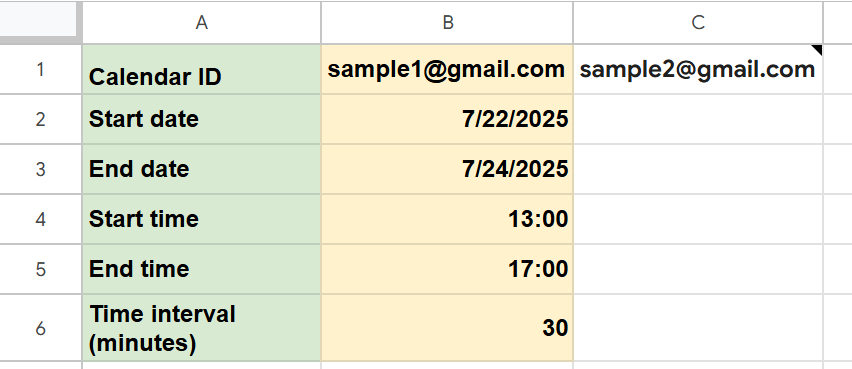
Open a new Google Spreadsheet and enter the following:
| Input Fields | |
|---|---|
| B1 | Google Calendar ID(s) you want to check (If you have multiple calendars, enter the IDs from B1 to the right) |
| B2 | Start date of the period to check |
| B3 | End date of the period to check |
| B4 | Start time of available slots |
| B5 | End time of available slots |
| B6 | Time interval (minutes) (For example, entering “30” will display available time slots in 30-minute increments) |
For this example, we’ll name the sheet Check Availability.
(The script will refer to this sheet by name.)
- Enter the start time (cell B4) and end time (cell B5) for the free time slots as text strings (e.g., 09:00), not as numbers or Google Sheets’ time format.
- If you use only numbers or the default time format, the script may not read them correctly.
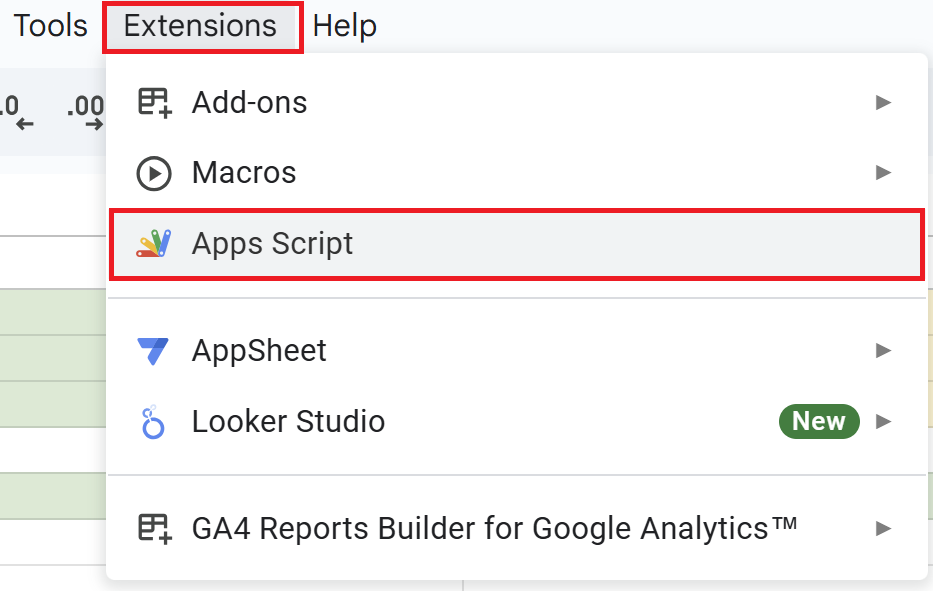
Open your Google Spreadsheet, click on “Extensions” in the menu, and select “Apps Script” to open the editor.
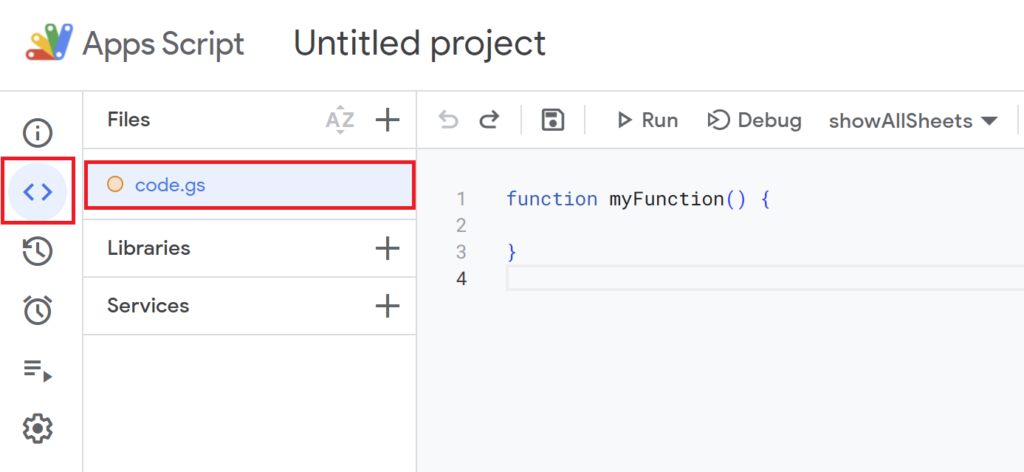
function myFunction(){
}
is included from the beginning, so delete it and paste the previous script.
function findCommonFreeTime() {
const sheetName = "Check Availability"; // Sheet name
const sheet = SpreadsheetApp.getActiveSpreadsheet().getSheetByName(sheetName);
if (!sheet) {
Logger.log(`Error: Sheet "${sheetName}" not found. Please create the sheet in your spreadsheet.`);
return;
}
const startDate = new Date(sheet.getRange("B2").getValue()); // Start date
const endDate = new Date(sheet.getRange("B3").getValue()); // End date
// The interval is no longer needed for splitting free times, so it's not used below
// const interval = parseInt(sheet.getRange("B6").getValue());
const calendarIds = sheet.getRange("B1:1").getValues()[0].filter(id => id);
if (calendarIds.length === 0) {
Logger.log("Error: No calendar ID specified. Please enter the calendar IDs starting from cell B1.");
return;
}
// Get start/end time from B4/B5
let startTimeStr = sheet.getRange("B4").getValue();
let endTimeStr = sheet.getRange("B5").getValue();
if (startTimeStr instanceof Date) {
startTimeStr = Utilities.formatDate(startTimeStr, Session.getScriptTimeZone(), "H:mm");
}
if (endTimeStr instanceof Date) {
endTimeStr = Utilities.formatDate(endTimeStr, Session.getScriptTimeZone(), "H:mm");
}
let startHour = 0, startMinute = 0, endHour = 23, endMinute = 59;
if (startTimeStr) {
const [sHour, sMinute] = startTimeStr.split(":").map(Number);
startHour = sHour;
startMinute = sMinute || 0;
}
if (endTimeStr) {
const [eHour, eMinute] = endTimeStr.split(":").map(Number);
endHour = eHour;
endMinute = eMinute || 0;
}
const weekdays = ["Sun", "Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat"];
const freeTimeSlots = [];
for (let day = new Date(startDate); day <= endDate; day.setDate(day.getDate() + 1)) {
const dayString = Utilities.formatDate(new Date(day), Session.getScriptTimeZone(), "MM/dd/yyyy");
const weekdayString = `(${weekdays[day.getDay()]})`;
const formattedDate = `${dayString} ${weekdayString}`;
// Set daily start/end time
const dayStart = new Date(day);
dayStart.setHours(startHour, startMinute, 0, 0);
const dayEnd = new Date(day);
dayEnd.setHours(endHour, endMinute, 59, 999);
// 1. Gather all events from all calendars into one array
let allEvents = [];
calendarIds.forEach(calendarId => {
const calendar = CalendarApp.getCalendarById(calendarId);
if (!calendar) return;
const events = calendar.getEvents(dayStart, dayEnd);
events.forEach(event => {
allEvents.push({
start: event.getStartTime(),
end: event.getEndTime()
});
});
});
// 2. Sort events by start time
allEvents.sort((a, b) => a.start - b.start);
// 3. Merge overlapping events (to get ALL busy periods)
let mergedEvents = [];
allEvents.forEach(event => {
if (!mergedEvents.length) {
mergedEvents.push({ start: event.start, end: event.end });
} else {
let last = mergedEvents[mergedEvents.length - 1];
if (event.start <= last.end) {
// Overlapping
last.end = new Date(Math.max(last.end.getTime(), event.end.getTime()));
} else {
mergedEvents.push({ start: event.start, end: event.end });
}
}
});
// 4. Calculate free time slots between merged busy periods
let freeTimes = [];
let prevEnd = new Date(dayStart);
mergedEvents.forEach(event => {
if (event.start > prevEnd) {
freeTimes.push({ start: new Date(prevEnd), end: new Date(event.start) });
}
prevEnd = new Date(Math.max(prevEnd.getTime(), event.end.getTime()));
});
if (prevEnd < dayEnd) {
freeTimes.push({ start: new Date(prevEnd), end: new Date(dayEnd) });
}
// 5. Output each free time slot as a single line (not split by interval)
freeTimes.forEach(time => {
const startStr = Utilities.formatDate(time.start, Session.getScriptTimeZone(), "H:mm");
const endStr = Utilities.formatDate(time.end, Session.getScriptTimeZone(), "H:mm");
freeTimeSlots.push([formattedDate, `${startStr} - ${endStr}`]);
});
}
// Output to sheet
sheet.getRange("A9:B").clear();
if (freeTimeSlots.length === 0) {
sheet.getRange("A9:B9").setValues([["No available time slots found.", ""]]);
} else {
const outputRange = sheet.getRange(9, 1, freeTimeSlots.length, 2);
outputRange.setValues(freeTimeSlots);
}
// Header styling
const headerRange = sheet.getRange("A8:B8");
headerRange.setValues([["Date", "Free Time"]]);
headerRange.setHorizontalAlignment("center");
headerRange.setBackground("#e6f4ea");
const timeColumnRange = sheet.getRange(9, 2, freeTimeSlots.length, 1);
timeColumnRange.setHorizontalAlignment("right");
Logger.log(`Common free time slots have been output as single intervals per row.`);
}
Script Overview
- Retrieving Sheet and Configuration Settings
-
const sheetName = "Check Availability"; // Sheet name const sheet = SpreadsheetApp.getActiveSpreadsheet().getSheetByName(sheetName); if (!sheet) { Logger.log(`Error: Sheet "${sheetName}" not found. Please create the sheet in your spreadsheet.`); return; } const startDate = new Date(sheet.getRange("B2").getValue()); // Start date const endDate = new Date(sheet.getRange("B3").getValue()); // End date // Get values from B4 and B5 for the daily available time window let startTimeStr = sheet.getRange("B4").getValue(); let endTimeStr = sheet.getRange("B5").getValue(); if (startTimeStr instanceof Date) { startTimeStr = Utilities.formatDate(startTimeStr, Session.getScriptTimeZone(), "H:mm"); } if (endTimeStr instanceof Date) { endTimeStr = Utilities.formatDate(endTimeStr, Session.getScriptTimeZone(), "H:mm"); }TThe script begins by retrieving the specified sheet where the settings and results are managed.
It checks that the sheet exists, then reads the search period (start and end dates) and the daily available time window (from cells B2, B3, B4, and B5).
If the start or end time is entered as a date object, it is converted to a string in “HH:mm” format for consistent processing. - Retrieving Calendar IDs
-
const calendarIds = sheet.getRange("B1:1").getValues()[0].filter(id => id); if (calendarIds.length === 0) { Logger.log("Error: No calendar ID specified. Please enter the calendar IDs starting from cell B1."); return; }The script collects all Google Calendar IDs that are entered from cell B1 to the right (across row 1).
If no calendar IDs are specified, it outputs an error message and stops execution.
This ensures that the script only proceeds when there is at least one calendar to check for availability. - Setting the Time Range
-
// Get values from B4 and B5 for the daily available time window let startTimeStr = sheet.getRange("B4").getValue(); let endTimeStr = sheet.getRange("B5").getValue(); // Convert Date objects to string if necessary if (startTimeStr instanceof Date) { startTimeStr = Utilities.formatDate(startTimeStr, Session.getScriptTimeZone(), "H:mm"); } if (endTimeStr instanceof Date) { endTimeStr = Utilities.formatDate(endTimeStr, Session.getScriptTimeZone(), "H:mm"); } let startHour = 0, startMinute = 0, endHour = 23, endMinute = 59; if (startTimeStr) { const [sHour, sMinute] = startTimeStr.split(":").map(Number); startHour = sHour; startMinute = sMinute || 0; } if (endTimeStr) { const [eHour, eMinute] = endTimeStr.split(":").map(Number); endHour = eHour; endMinute = eMinute || 0; }The script retrieves the start and end times from cells B4 and B5, and converts them to a usable string format if needed.
If no times are entered, it defaults to 0:00 (midnight) as the start and 23:59 as the end time.
The script then splits these into hour and minute values for later use. - Calculating Free Time for Each Date
-
for (let day = new Date(startDate); day <= endDate; day.setDate(day.getDate() + 1)) { // Format date for output const dayString = Utilities.formatDate(new Date(day), Session.getScriptTimeZone(), "MM/dd/yyyy"); const weekdayString = `(${weekdays[day.getDay()]})`; const formattedDate = `${dayString} ${weekdayString}`; // Set daily time window const dayStart = new Date(day); dayStart.setHours(startHour, startMinute, 0, 0); const dayEnd = new Date(day); dayEnd.setHours(endHour, endMinute, 59, 999); // Gather and merge all calendar events let allEvents = []; calendarIds.forEach(calendarId => { const calendar = CalendarApp.getCalendarById(calendarId); if (!calendar) return; const events = calendar.getEvents(dayStart, dayEnd); events.forEach(event => { allEvents.push({ start: event.getStartTime(), end: event.getEndTime() }); }); }); allEvents.sort((a, b) => a.start - b.start); let mergedEvents = []; allEvents.forEach(event => { if (!mergedEvents.length) { mergedEvents.push({ start: event.start, end: event.end }); } else { let last = mergedEvents[mergedEvents.length - 1]; if (event.start <= last.end) { last.end = new Date(Math.max(last.end.getTime(), event.end.getTime())); } else { mergedEvents.push({ start: event.start, end: event.end }); } } }); // Calculate free time slots between busy periods let freeTimes = []; let prevEnd = new Date(dayStart); mergedEvents.forEach(event => { if (event.start > prevEnd) { freeTimes.push({ start: new Date(prevEnd), end: new Date(event.start) }); } prevEnd = new Date(Math.max(prevEnd.getTime(), event.end.getTime())); }); if (prevEnd < dayEnd) { freeTimes.push({ start: new Date(prevEnd), end: new Date(dayEnd) }); } // Output each free time slot freeTimes.forEach(time => { const startStr = Utilities.formatDate(time.start, Session.getScriptTimeZone(), "H:mm"); const endStr = Utilities.formatDate(time.end, Session.getScriptTimeZone(), "H:mm"); freeTimeSlots.push([formattedDate, `${startStr} - ${endStr}`]); }); }For each day in the specified date range, the script gathers all events from all calendars, merges overlapping busy periods, and calculates the available free time slots.
Each common free slot is then output as a single, continuous interval. - Retrieving Calendar Events and Calculating Free Time
-
// Gather and merge all calendar events let allEvents = []; calendarIds.forEach(calendarId => { const calendar = CalendarApp.getCalendarById(calendarId); if (!calendar) return; const events = calendar.getEvents(dayStart, dayEnd); events.forEach(event => { allEvents.push({ start: event.getStartTime(), end: event.getEndTime() }); }); }); allEvents.sort((a, b) => a.start - b.start); // Merge overlapping events to get busy periods let mergedEvents = []; allEvents.forEach(event => { if (!mergedEvents.length) { mergedEvents.push({ start: event.start, end: event.end }); } else { let last = mergedEvents[mergedEvents.length - 1]; if (event.start <= last.end) { last.end = new Date(Math.max(last.end.getTime(), event.end.getTime())); } else { mergedEvents.push({ start: event.start, end: event.end }); } } }); // Calculate free time slots between busy periods let freeTimes = []; let prevEnd = new Date(dayStart); mergedEvents.forEach(event => { if (event.start > prevEnd) { freeTimes.push({ start: new Date(prevEnd), end: new Date(event.start) }); } prevEnd = new Date(Math.max(prevEnd.getTime(), event.end.getTime())); }); if (prevEnd < dayEnd) { freeTimes.push({ start: new Date(prevEnd), end: new Date(dayEnd) }); }For each date, the script retrieves all calendar events for the specified time range across all selected calendars.
It then merges any overlapping events into busy periods.
By identifying the gaps between these busy periods, the script calculates the common free time slots—intervals when everyone is available.
These free time slots are stored as start and end times for later output. - Outputting Common Free Time to the Spreadsheet
-
sheet.getRange("A9:B").clear(); if (freeTimeSlots.length === 0) { sheet.getRange("A9:B9").setValues([["No available time slots found.", ""]]); } else { const outputRange = sheet.getRange(9, 1, freeTimeSlots.length, 2); outputRange.setValues(freeTimeSlots); } // Header styling const headerRange = sheet.getRange("A8:B8"); headerRange.setValues([["Date", "Free Time"]]); headerRange.setHorizontalAlignment("center"); headerRange.setBackground("#e6f4ea"); const timeColumnRange = sheet.getRange(9, 2, freeTimeSlots.length, 1); timeColumnRange.setHorizontalAlignment("right"); -
The script clears any previous results and writes the new list of common free time slots starting from cell A9.
If no common free time is found, a message is displayed.
The header row is styled for readability.
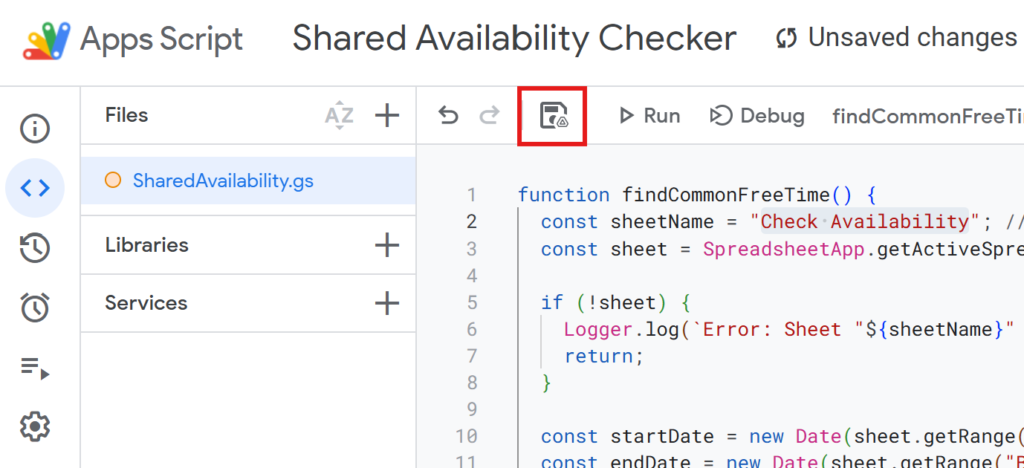
After writing your script, give it a descriptive name and save it.
(For example: SharedAvailability)
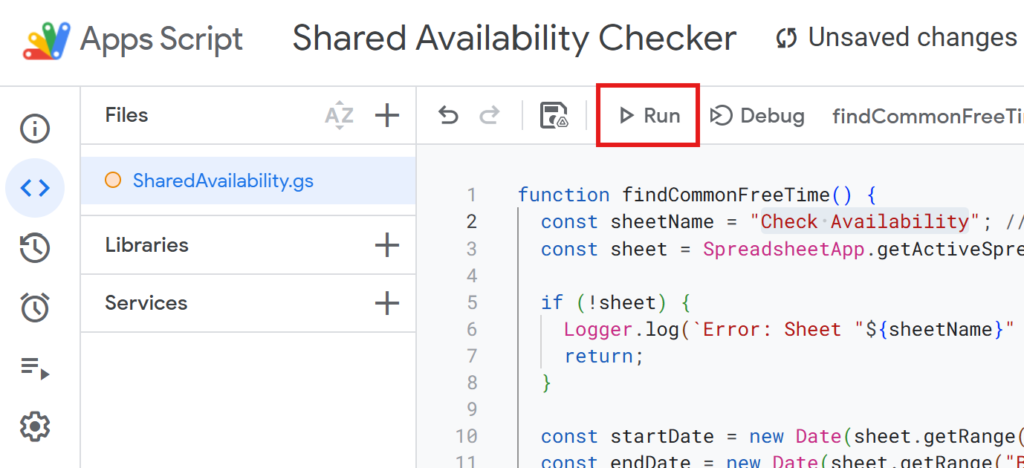
When you run the script, it will search each Google Calendar for overlapping availability and list all common free time slots.
If you’re running the script for the first time, you need to authorize it.
Therefore, press “Review Permissions.“
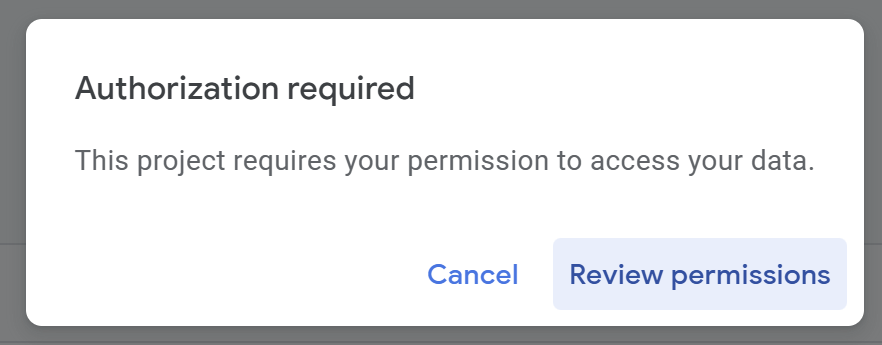
Detailed Authorization Steps
Press “Advanced.”
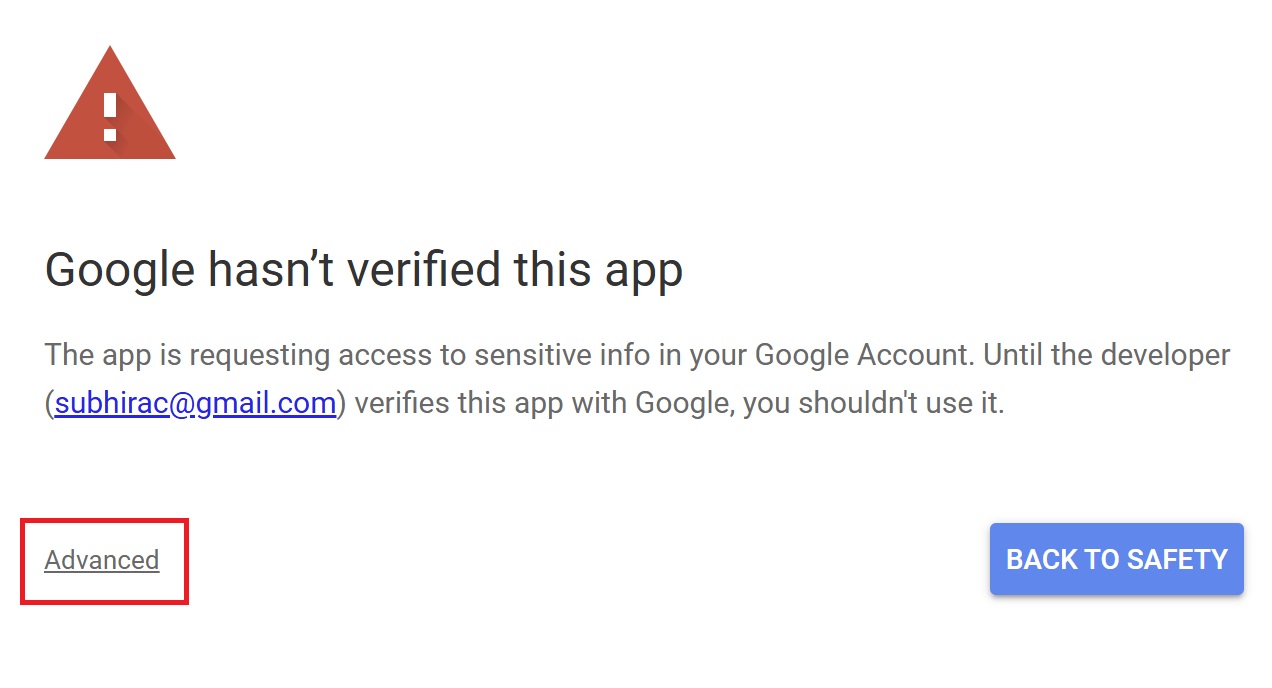
Press “Go to Untitled project (Unsafe).”
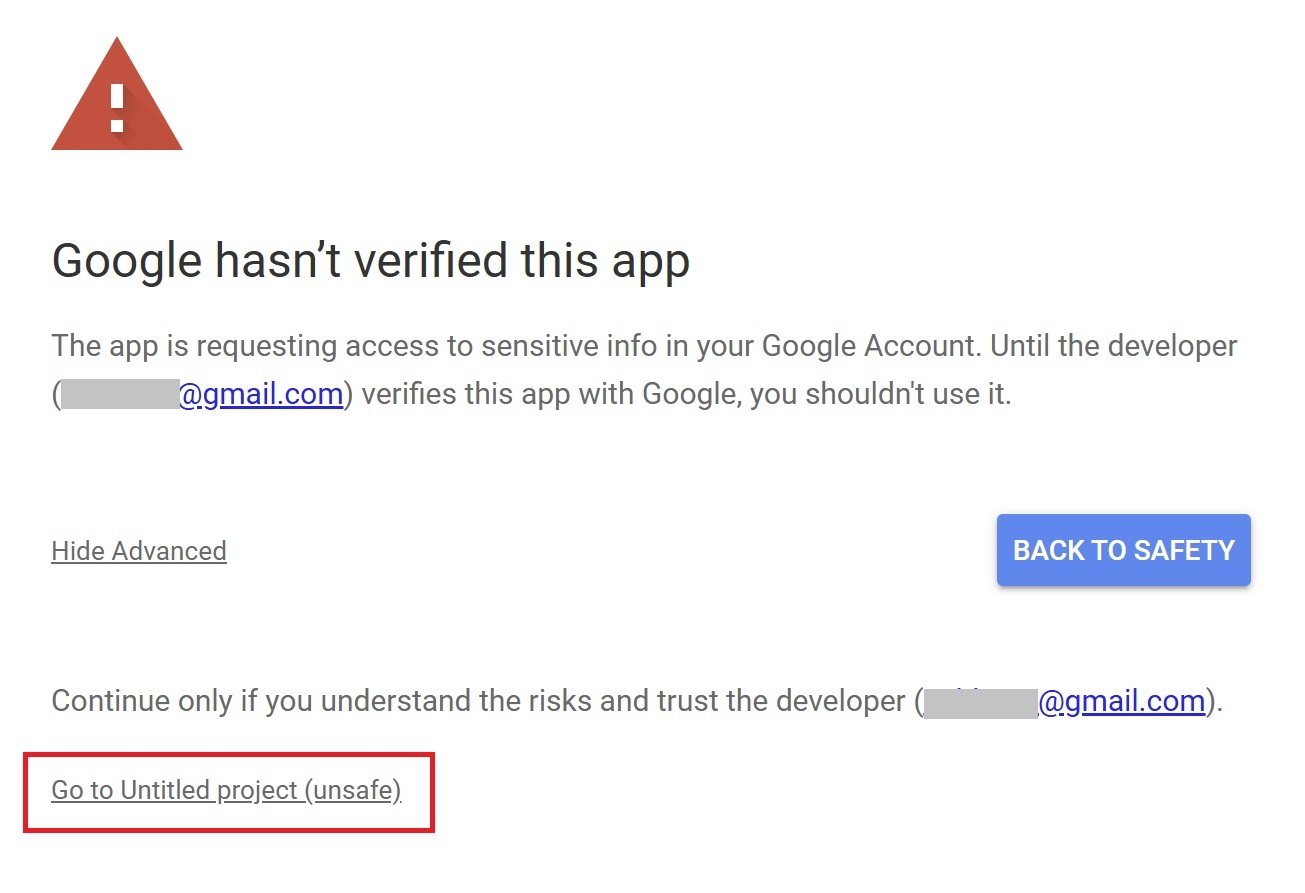
After that, press “Allow.”
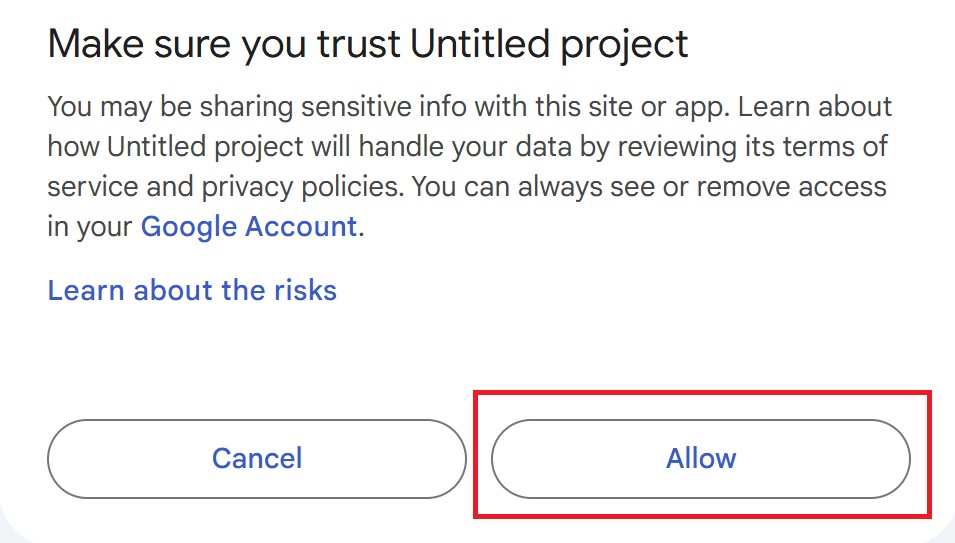
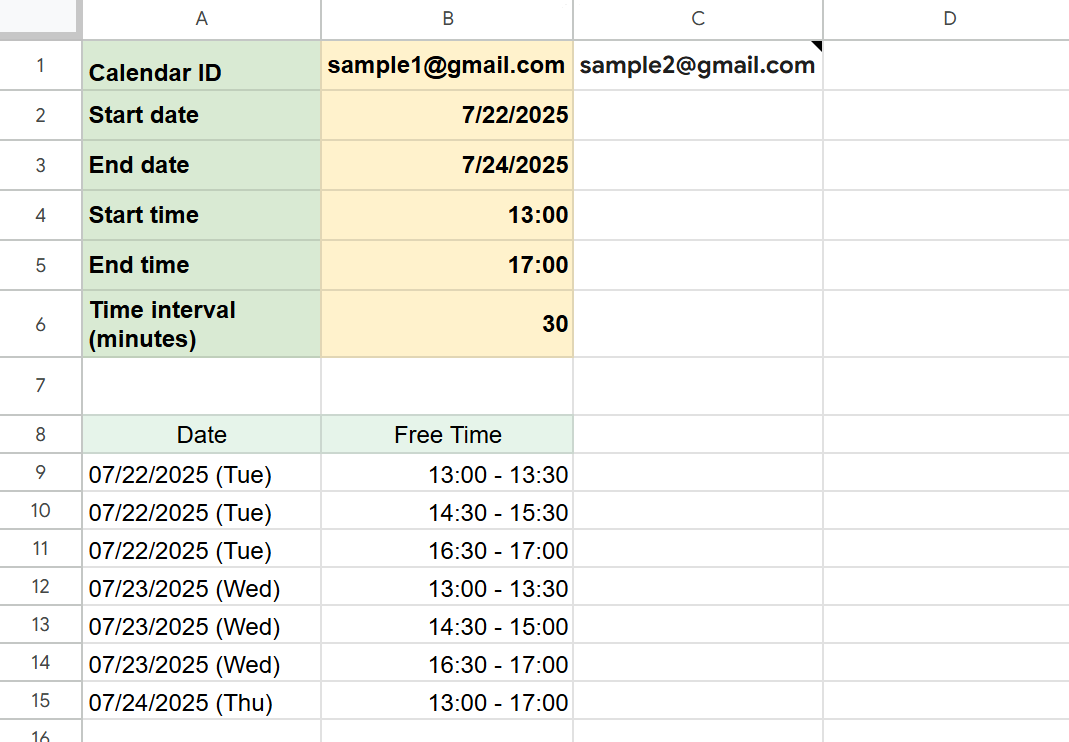
Once the script runs successfully, the shared free time slots for each date will be displayed in the “Check Availability” sheet starting from row 9.
If everyone’s schedules overlap and no common free time exists, a message saying “No available time slots found.” will appear.
Notes
- Handling All-Day Events
-
Be aware that all-day events (such as “Home” or “Out of Office” marked as all-day in the calendar) can interfere with the free time extraction process. If these events overlap with other schedules, the script may not be able to identify any available time slots.
To prevent this, consider changing all-day events to time-specific events, or limit the calendars included in the extraction to only those relevant for finding shared availability.
- Setting the Time Range
-
When specifying the time range for free time extraction (e.g., 10:00–18:00), please enter the start time (cell B4) and end time (cell B5) as plain text (e.g., “10:00”).
If you enter times using Google Sheets’ time format, the script may interpret the values incorrectly and fail to extract the correct time slots.
-
If cells B4 (start time) and B5 (end time) are left blank, the script will search for free time across the entire 24-hour period.
- Checking Your Calendar IDs
-
If your Calendar IDs are not entered correctly, the script may fail to retrieve the right data.
When working with multiple calendars, make sure to enter each Calendar ID horizontally from cell B1 to the right.
Double-check that all required IDs are included and correctly typed.
Conclusion
By using Google Apps Script to extract and organize common free time from Google Calendar into a spreadsheet, you can efficiently check and manage the availability of multiple team members.
This approach streamlines the process of scheduling meetings or appointments and helps eliminate wasted time spent coordinating everyone’s calendars.
Just remember: if there are any all-day events, the script may not be able to find common free time slots—so keep this in mind when reviewing the results.

Our company offers support for improving work efficiency through the use of Google Apps Script.
If you need assistance with Google Apps Script customization or error resolution, please feel free to contact us.
We are fully committed to supporting your business improvements.
Contact us here








Comments